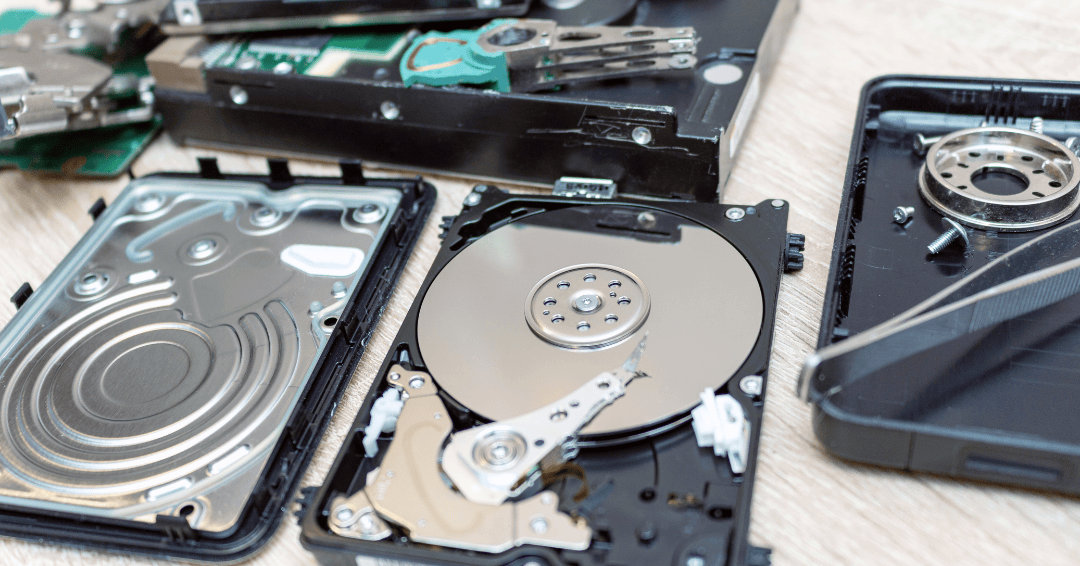
Despite SSDs becoming mainstream, many businesses are still using dated approaches to destroying the data stored on these drives
When it’s time to upgrade your Information Technology (IT) Assets, you will be faced with the issue of how to deal with the data held on them.
Over time your hardware will have built up an array of stored data, right back from when it was first switched on. You have to handle this data correctly to prevent any data breaches and/or regulatory violations.
Typically, there are two kinds of hard drives which store data on IT Assets: hard disk drives (HDD’s) and solid-state drives (SSD).
How do Solid State Drives and a Hard Disk Drives store data?
HDDs contain one or more rotating disks, relying on magnetic storage; while SSD’s have no mechanical or moving parts, and use flash memory. The data in SSDs is sorted in chips, which are becoming increasingly powerful, but also smaller as technology progresses.
Because of their different construction, these two very different types of drives require different destruction techniques.
So, what methods are available to destroy the data held on SSDs?
Before we jump in to whether its best practise to shred, puncture or degauss SSDs; it’s important to understand that these are all techniques which once complete, render the media unusable. Where possible, it is preferable to electronically wipe hardware using a software based data erasure technique; this allows the IT Asset to be remarketed which is better financially and environmentally.
For physical data erasure, to remove the data contained on SDDs, each chip contained within the SSD itself must be physically destroyed.
This differs to HDDs which use magnetic discs, containing data held on ‘CD like‘ platters, which can be data cleansed using degaussing (or by a physical hard drive destruction process).
Shredding
 SSDs can be shredded in a mechanical process typically called hard drive shredding. These machines contain counter rotating blades, and the material fed into these machines is forced through these cutting blades, physically destroying the hard drive.
SSDs can be shredded in a mechanical process typically called hard drive shredding. These machines contain counter rotating blades, and the material fed into these machines is forced through these cutting blades, physically destroying the hard drive.
However, as it is possible to recover data from small intact fragments of SSD drives, the shredder or puncturing machine used, must meet the needs specific to the materials which are being data erased.
Typically, where a shredder is concerned, this means using a shred size small enough to ensure the destruction of individual chips.
The resulting output is miniscule granules of shredded material, the exact size of which depends on the capability of the shredder. It is recommended that shred sizes for SSDs be smaller than 10mm to ensure the chips are destroyed.
Puncturing
 Puncturing SSDs is also a physical process, but one that differs slightly to shredding. Drives are placed into machinery containing a press, which punches multiple pins into the hard drive, and the chips contained within them, annihilating the data contained.
Puncturing SSDs is also a physical process, but one that differs slightly to shredding. Drives are placed into machinery containing a press, which punches multiple pins into the hard drive, and the chips contained within them, annihilating the data contained.
After puncturing all memory chips are destroyed in that process and the drive is littered with holes.
Degaussing
Degaussing will not erase the data held on Solids State Drives (SSD)’s, as a solid-state drive stores data electronically.
It is an efficient way of erasing the data held on Hard Disk Drives (HDD)’s, floppy disks, magnetic tapes on open reels or cassettes; as they store data using layers of magnetic fields, disrupted and eliminated by degaussing.
A degausser works by applying alternating fields of powerful magnetic amplitude, which removes the drives magnetic properties or rearranges the magnetic data pattern, irrecoverably removing the data.
Conclusion
To ensure the regulatory compliance and secure destruction of data on solid state drives (SSDs), both shredding and puncturing can successfully meet the data sanitisation compliance required, while degaussing cannot.
However, both respective techniques (shredding and puncturing), must be completed to the correct specification, to ensure the physical destruction of the chips within those hard drives and offering you complete peace of mind.
Data security needs to be threaded into every aspect of how your aged IT Assets are handled. Issues with data destruction not only carry heavy fines, but there is also the almost immeasurable cost to your brands reputation resulting from any subsequent breach.